Important Topics
Table of Contents
- 1. In the news
- 2. Geography
- 3. Economy
- 4. Arts
- 5. Punjabi Literature
- 6. Anglo-Sikh Wars
- 7. Rights, Duties, Directives
- 8. Amendments
- 9. Judiciary
- 10. Revolutionary Trends
- 11. Constitution
- 12. Global programmes
- 13. Important Events in 2018
- 14. Ramsar Convention on Wetlands 1971
- 15. Punjab – Geography & Environment
1 In the news
1.1 Indices 2018
| Creator | Name | Measures | Position of India | Previous Position | BRICS | SAARC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World Bank | Ease of Doing Business | 100/190 | 130 | |||
| World Bank | Starting a Business | |||||
| World Bank | Index of Investor Protection | |||||
| Transparency International | Corruption Perception Index | 76/168 | ||||
| Save the Children | Child Development Index | |||||
| Economist Intelligence Unit | Democracy Index | |||||
| Charities Aid Foundation | Were to born Index | |||||
| UNDP | Education Index | |||||
| UNDP | Gender Empowerment Measure | |||||
| UNDP | Gender Inequality Index | reproductive health, empowerment, economic activity | ||||
| UNDP | HDI | Health, education, wealth | ||||
| UNDP | Human Poverty Index | |||||
| The Access Initiative (TAI) & the World Resources Institute (WRI) | Environmental Democracy Index | |||||
| World Economic Forum (WEF) | Global Gender Gap Index | |||||
| WEF | Environmental Performance Index | |||||
| WEF | Global Competitive Index | |||||
| WEF | Network Readiness Index | |||||
| WEF | Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index | |||||
| International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) | Global Hunger Index | |||||
| Cornell, INSEAD, WIPO | Global Innovation Index | |||||
| Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP) | Global Peace Index | |||||
| Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP) | Global Terrorism Index | |||||
| Reporters Without Borders | Press Freedom Index | |||||
| OECD Development Center | Social Institutions and Gender Index | |||||
1.2 Forums & Meets
| Name | Year | Host | Agenda | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1.3 Female Fighter Pilots (Inspector Cooperatives 2018)
First batch of 3 Indian fighter pilots:
- Avani Chaturvedi – MP
- Bhavana Kanth – Bihar
- Mohana Singh – Rajasthan
1.4 Sports
1.4.1 Fifa World Cup
| Year | Host |
|---|---|
| 2018 | Russia |
| 2022 | Qatar |
1.4.2 Cricket World Cup
| Year | Host | Winner |
|---|---|---|
| 2011 | India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh | India |
| 2015 | Australia | Australia |
| 2019 | England & Wales | --- |
2 Geography
2.1 Latitudes
2.1.1 Tropic of Cancer
- Asia – Passes through 8 countries
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Oman
- India
- Bangladesh
- Myanmar
- China
- Taiwan
- Africa
- Algeria
- Niger
- Libya
- Egypt
- India – Passes through 8 states
- Gujarat
- Rajasthan
- Madhya Pradesh
- Chhatissgarh
- Jharkhand
- West Bengal
- Mizoram
- Tripura
- Europe
- (none)
- North America
- Mexico
- Bahamas
- Water Bodies
- Atlantic Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- Red Sea
- Arabian Sea
- Taiwan Strait
2.1.2 Tropic of Capricorn
2.1.3 Equator
3 Economy
3.1 Sustainable development
As given in the report by the Brundtland Commission title Our Common Future:
"meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the needs of the future generation"
3.2 Types of Goods
| Type | Relation between demand and income/price | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Normal (Luxury) Goods | demand ∝ income | |
| Inferior Goods | demand ∝ 1/income | kerosene oil |
| Ordinary Goods | demand ∝ 1/price (follow law of demand) | sugar, tea, chicken, etc. |
| Giffen Goods | demand ∝ price (products are cheap) | staple foods, Ireland potato famine |
| Veblen Goods | demand ∝ price (products are expensive) | goods indicative of status, designer goods, famous works of art |
Both Giffen and Veblen goods violate the law of demand.
| Merit Goods | these goods have positive externalities | education, vaccination, socila infrastructure |
| in a free market, there is underconsumption | ||
| Demerit goods | these goods have negative externalities | alcohal, cigarettes, drugs, etc. |
| in a free market, there is overconsumption |
3.3 Macroeconomic Growth Indicators
| Indicator | Formula | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| GDP (at market prices) | Market value of goods and services for final consumption | value of goods and services produced within the territory of a nation |
| NDP (at market prices) | NDP (MP) = GDP (MP) - Depreciation | |
| GDP (at factor costs) | GDP (FC) = GDP (MP) + subsidies - indirect taxes | |
| NDP (at factor costs) | NDP (FC) = NDP (MP) + subsidies - indirect taxes | |
| GNP (at market prices) | GNP (MP) = GDP (MP) + Net Factor Income from abroad | value of goods and services produced by the nationals of a nation |
| NNP (at market prices) | NNP (MP) = GNP (MP) - depreciation | |
| GNP (at factor costs) | GNP (FC) = GNP (MP) + subsidies - indirect taxes | |
| NNP (at factor costs) | NNP (FC) = NNP (FC) + subsidies - indirect taxes | also known as National Income |
Since cost of depreciation varies across nations, it is not used for comparisons or competitive economics. GDP is used for that purpose.
GDP is calculated by Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) of Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI). CSO is the data processing wing of this ministry while NSSO is the data collection wing.
GNP is calculated by World Bank, IMF, etc.
3.3.1 Income of a nation
- Nominal Income
Calculated at current prices, inflation is not considered.
- Real income
refers to National income expressed in terms of level of prices of a particular year taken as base. At present the base year for GDP, IIP, WPI is 2011-12. It is set to be changed to 2017-18 in the coming months.
GDP Deflator = (nominal income / real income) x 100 - 100
GDP deflator gives a measure of inflation.
- Per capital income
per capital income = NNP/total population
3.4 Curves
| Name of the Curve | Relationships | Image | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demand curve | Demand and prices | img:https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/7a/Supply-and-demand.svg | negative/downward slope |
| Supply Curve | Supply and prices | img:https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/40/Supply.gif | positive slope |
| Laffer Curve | Tax rate and revenue collected | img:http://bulgariaanalytica.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/laffer-curve.png | inverted parabola |
| Kuznets Curve | Income per capita and Inequality | img:https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/6b/Kuznets_curve.png | inverted parabola |
| Lorenz Curve | Distribution of wealth | img:https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/59/Economics_Gini_coefficient2.svg | |
| Philips Curve | Rate of unemployment and rise in wages (later inflation) | img:https://www.economicshelp.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/phillips-curve-600x400.png | |
| Rahn Curve | Size of govt and economic performance | img:https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ac/Rahn_Curve.svg | |
| Great Gatsby Curve | Inequality and intergenerational social mobility | / | upward sloping line |
4 Arts
4.1 Natya Shastra
Natya Shastra by Bharat Muni is a Sanskrit text on performing arts written between 200 BC and 200 AD. It covers dancing, acting, drama, etc.
It gives the concept of rasa in aesthetics:
| Name of the Rasa | Associated emotion |
|---|---|
| Shringar | Love |
| Raudra | Anger |
| Hasya | Comic |
| Bhibhats | Disgust |
| Karuna | Compassion |
| Vira | Heroism |
| Bhayanak | Fear |
| Adhbuta | Wonder |
4.2 8 Classical Dances
The Sangeet Natak Akademi recognizes 8 classical dances
| Name of the Dance | State | Themes | Recognition | Remarks | Instruments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bharatnatyam | Tamil Nadu | traditionally associated with ideas of Vaishnavism, Shaktism, Shaivism | Fixed upper torso, knees bent, detailed gestures of facial muscles, hands | oldest classical dance | |
| Kathakali | Kerala | folk mythologies, religious legends, spiritual ideas from epics, puranas | elaborate makeup | a kind of story play | |
| Mohiniyattam | Kerala | solo, delicate, feminine | |||
| Kuchipudi | Andhra Pradhesh, Telangana | Krishan-oriented, Vaishanvism-centric | mridangam, cymbals, veena, flute, tanpura | ||
| Odissi | Odisha | Jaggnath (Vaishnavism), Shiva, Surya, Shakti | |||
| Sattriya | Assam | khol (asymmetric drum), cymbals, flute | |||
| Manipuri | Manipur | ||||
| Kathak | Northern and Western India |
4.3 Semi-classical dances
Some scholars suggest Chhau, Yakshgana and Bhagvata Mela should be added to the list of classical dances. They are sometimes referred to as semi-classical dances.
| Name of the Dance | State | Themes | Recognition | Remarks | Instruments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chhau | Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha | spring, shaivism, shaktism, vaishnavism | traditionally men only | ||
| Yakshagana | Karnataka | Ramayana, Mahabharata, Gita | |||
| Bhagvata Mela | Tamil Nadu |
5 Punjabi Literature
| Writer | Notable Works | Notable Ideas / Inventions | Other Affiliations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bhai Veer Singh | Mere Sayia Jio (sahitya academy award) | Father of modern Punjabi literature | Khalsa Samachar, Nirguneara |
| Rana Surat Singh, Lehra de haar, Matak Hulare, Bijlia de haar | |||
| Preet Veena, Kamdi Kalai | |||
| Prof Puran Singh | Khulle Asmani Rang, Khulle Ghund, Jawaan Punjab De, Puran Nath Jogi | Free verse (khulli kavita) | |
| Prof Mohan Singh | Saave Pattar, Chhato di beri, Saida te Sabza, Kasumbhra | Panj Darya – a monthly | |
| Amrita Pritam | Kaagaz te Canvas (Gianpeeth) | All India Radio | |
| Sunehre (Sahitya Academy award) | |||
| Naagmani, Trinjn | |||
| Novels – Dr Dev, Pinjar te Aalna | |||
| Harbhajan Singh | Na Dhuppe Na Chhave (Sahitya academy award) | ||
| Shiv Kumar Batalvi | Loona (sahitya academy award) | ||
6 Anglo-Sikh Wars
6.1 First Anglo-Sikh War (1845-46)
Lord Hardinge was the Governor-General at the time.
| Battle | Sikh Leader | British Leader | Victor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mudki | Lal Singh (PM) | Sir Hugh Gough | British |
| Firozpur | Tej Singh (C-i-C) & Lal Singh | Sir Hugh Gough | British |
| Buddhewal | Ranjodh Singh Majithia | Sir Henry Smith | Sikhs |
| Aliwal | Ranjodh Singh Majithia | Sir Henry Smith | British |
| Sabraon | Lal Singh, Tej Singh, Sham Singh Attariwala | Sir Henry Smith | British |
6.1.1 Treaty of Lahore
- Maharaja Dalip Singh as sovereign of Lahore and his mother Rani Jinda as regent of the king
- Indemnity of Rs. 1.5 crore to be paid by Sikhs
- Territory between Beas and Satluj (Jullundur Doab) annexed by British, i.e. both banks of Satluj
- Jammu and Kashmir handed over to Gulab Singh in lieu of Rs. 1 crore by separate treaty (Treaty of Amritsar 1846)
6.1.2 Treaty of Bhairowal
- Rani Jinda removed
- Council of Regency comprising 8 Sardars and Sir Henry Lawrence as British resident till the king turned 16.
- Stationing of British forces at Lahore (Rs. 22 lakh to be paid by Sikhs)
- British troops could pass through Punjab, take and garrison any fort
6.2 Second Anglo-Sikh War (1848-49)
Lord Dalhousie was the Governor-General at that time.
| Battle | Sikh Leader | British Leader | Victor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ramnagar | Sher Singh Attariwala | Sir Gough | Sikhs |
| Chillianwala | Sher Singh Attariwala | Sir Gough | Sikhs |
| Multan | Mul Raj | General Whish | British |
| Gujrat | Chatar Singh & Sher Singh Attariwala | Sir Gough | British |
Battle of Chillianwala was the bloodiest battle fought by the British in India. It was a blow to their prestige.
6.2.1 Lord Dalhousie's proclamation 1849
It declared Punjab to be a part of the British Empire in India and disposed of Maharaja Dalip Singh to UK with an annual pension.
7 Rights, Duties, Directives
7.1 Funamental Duties
- On the recommendations of Swaran Singh Committee, added as Part IV-A (Art 51-A) in 42nd Amendment
- In 1992 SC allowed reasonable restrictions to Art 14 (equality before law) and Art 19 (six freedoms) to give effect to a fundamental duty
- Fundamental duties can be enforced by a law passed in the Parliament
7.2 Fundamental Rights & Directive Principles
| Fundamental Rights | Directive Principles |
|---|---|
| They are negative – forbid the state from doing something | Always positive |
| They are justiciable, i.e. legally enforceable by courts in case of violation – Do not require legislation for implementation | Not legally enforceable – Require legislation for implementation |
| Aim of establishing political democracy in the country | Aim of establishing social and economic democracy |
| Legal sanction | Moral and political sanction |
| Welfare of individual – personal and individualistic | Welare of community – solitarian and socialistic |
| Law in violation of Fundamental Rights can be declared null and void | Law in violation of Directive Principles can't be declared invalid; however, a law can be upheld on the ground that it gives effect to a directive principle |
7.3 Important Judgements
| Case | Verdict |
|---|---|
| Gokalnath Case 1967 | Parliament cannot abrogate Fundamental Rights by amendment |
| Keshvananda Bharati Case 1973 | Power of amendment of parliament is exercisable so far as it doesn't alter the basic structure |
| Minerva Mills Case 1980 | Fundamental rights cannot be abrogated in the name of Directive Priciples (except 39(b), (c)) or otherwise |
8 Amendments
| Amendment | Year | Content | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24th | 1971 | Parliament can amend fundamental rights as well as the procedure of amendment | 13, 368 |
| 25th | 1971 | DPSP 39(b),(c) have primacy over Fundamental rights | 31-C |
| 42nd | 1976 | DPSP: healthy development of children; free legal aid; workers' participation in management of industry; safeguard forests and wildlife | 39, 39-A, 43-A, 48-A |
| Fundamental Duties: Art 51-A (Part IV-A) added to the constitution | |||
| 44th | 1978 | DPSP: minimize inequalities | 48-A |
| 69th | 1991 | Delhi NCR | |
| 73rd | 1992 | Panchayati Raj | |
| 74th | 1992 | Local Bodies | |
| 86th | 2002 | Elementary education a fundamental right | 21-A |
9 Judiciary
9.1 Writs
| Name | Meaning | Issued to | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Habeas Corpus | produce the body | public authorities and private citizens | Produce a person who has been detained before court |
| Mandamus | We Command | a public official/body, corporation, inferior court, tribunal | Command issued to perform official duties he/she/it has failed to perform |
| Prohibition | To forbid | Judicial and quasi-judicial authority | Issued to lower court or tribunal to prevent it from exceeding jurisdiction or usurping jurisdiction it doesn't possess |
| Certiorari | To be certified or informed | Judicial, quasi-judicial authority and administrative authorities | to transfer a case pending before it to itself or to quash its order in a case, on grounds of excess of jurisdiction or error of law |
| Quo-warranto | By what authority? | Substantive public office of a permanent character created by statute/constitution | enquire into legality of claim of a person to a public office (prevents illegal usurpation of public office by a person) |
9.1.1 Prohibition vs Mandamus
| Mandamus | Prohibition |
|---|---|
| Directs towards doing something that has not been done | Directs towards not doing something because of lack of jurisdiction |
9.1.2 Prohibition vs Certiorari
| Prohibition | Certiorari |
|---|---|
| It is only preventive | Preventive as well as curative |
9.1.3 Quo Warranto
Unlike other 4 writs, this writ can be sought by any interested person rather than by the aggrieved person.
10 Revolutionary Trends
10.1 Phases
| Criteria | First Phase (1897-1914) | Second Phase (1923-47) |
|---|---|---|
| Inspiration | Italian unification | Russian Revolution |
| Initial fire | speeches of extremists | started after failure of NCM |
| Extent | Region-specific | pan-India |
| Organisations | Abhinav Bharat, Anushilan Samiti | Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA) |
| Participation | Religion/Caste specific | secular organsiations |
| Palpability | Underground | Gradual came out into the open |
| Publications | Yugantar | Sandhya |
| Methods of Suppression | Explosive Substances Act 1908, | |
| Newspapers Act 1908, 1910, | ||
| Seditious Meetings Act 1907, | ||
| Defence of India Rules 1915 | ||
| Termination | Defence of India Rules 1915 | |
| Achievements |
10.2 Associations
| Association | Region | Founder | Associated Persons | Adventures | Publications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitra Mela (later Abhinav Bharat) | Maharashtra | Mitra and Savarkar Brothers | |||
| Abhinav Bharat | Maharashtra | Veer Brothers | Praful Chakki, Khudiram Bose, | Kingsford Assasination attempt | |
| Anushilan Samiti | West Bengal (Dhaka) | P. Mitra | Aurobindo Ghosh, Barindra Ghosh, Rash Behari Bose | ||
| Jugantar Group | West Bengal (Calcutta) | Barin Ghosh | Jatindranath Mukherjee (Bagha Jatin) | ||
| Ghadar Party | HQ in San Francisco | Lala Har Dayal | Sohan Singh Bhakna, Kartar Singh Sarabha, Harnam Singh 'Tundilat', Kanshi Ram, Bhai Parmanand | ||
| Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA) | Pan-India (founded in Delhi) | Sachindranath Sanyal, Chandrashekhar Azad, Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev | Ram Prasad Bismil, Ashfaqullah Khan, Rajendra Lahiri, Roshan Singh, Rajguru, Battukeshwar Dutt | Kakori Conspiracy | The Revolutionary (its manifesto) |
| Assembly Bombing | |||||
| Murder of John Saunders | |||||
| Bombing of Viceroys special train |
10.3 HSRA
HSRA was founded in 1923 at a meeting in Feroz Shah Kotla
10.4 Some Related Incidents
| Komagatamaru | Ship contracted by Baba Gurdit Singh (Guru Nanak Trading Co. Malay) carrying 376 passengers faced abuse at Vancouver, Canada, and at every Port on their way back and finally violent incidents took place at Buj-Buj in West Bengal where some died and several arrested. |
| Curzon Wylie assassination | Madan Lal Dhingra caught and hanged |
11 Constitution
11.1 Constitutional Development
| Act | Landmark Changes | Provisions | Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Councils Act 1892 | Indirect elections | ||
| Indian Councils Act 1909 | Direct elections | ||
| (Minto-Morely Reforms) | Separate electorates for muslims | ||
| Lord S. P. Sinha made member in Executive Council of GG | |||
| Indian Councils Act 1919 | Provincial dyarchy (reserved and transfered subjects) | 3 Indians made members in executive council of GG | |
| (Montague-Chelmsford Reforms) | Bicameral legislature | ||
| Government of India Act 1935 | proposed an All India Federation with consent of princes representing 50% of population of princely states | Federal Provisions | A car with all brakes and no engine |
| idea of collective responsibility | bicameral legislature at center | ||
| Federal Court | Federal Court (created in 1937) | ||
| Federal Bank | Federal Bank (RBI Act 1937) | ||
| Emergency Powers | Three lists of subjects – Center, State, Concurrent | ||
| Concurrent list | |||
| Supplementary questions | Legislative Provisions | ||
| Members allowed to ask supplementary questions | |||
| Sindh & Odisha made separate states | Bulk of the budget could be voted upon | ||
| Burma and Aden (Yemen) separated from India | |||
| Emergency, veto and ordinance-making powers to GG | |||
11.2 Sources
| Provisions | Source Country |
|---|---|
| Rule of Law | UK |
| Legislative Procedure | UK |
| Parliamentary System | UK |
| Parliamentary Privileges | UK |
| Post of Vice President | US |
| Organisation & Powers of Supreme Court | US |
| Fundamental Rights | US |
| Judicial Review | US |
| Federal System | Canada, GoI Act 1935 |
| Emergency Provisions | Germany, GoI Act 1935 |
| Directive Principles of State Policy | Ireland |
| Fundamental Duties | Russia |
| Concurrent List | Australia |
| Republic | France |
| Constitution Amendment | South Africa |
| Procedure established by law | Japan |
11.3 Committees of the Constituent Assembly
| Committee | Chairman | Members |
|---|---|---|
| Union Constitution Committee | Nehru | |
| Union Procedure Committee | Nehru | |
| Provincial Constitution Committee | Sardar Patel | |
| Steering Committee | Rajendra Prasad | |
| Fundamental Rights Committee | J. B. Kriplani | |
| Minorities sub-committee | W. C. Mookherjee | |
| Business Committee | K. M. Munshee | |
| Drafting Committee | B. R. Ambedkar | N. Gopalaswami Ayangar, Alladi Krishnaswami Iyer, K. M. Munshi, Sayid Mohd Sadullah, Madhav Rao, Jagat Narain |
| Linguistic Provinces | S. K. Dhar | Panna Lal, Jagat Narain |
| Financial Provisions | N. R. Sarkar | V. S. Sundaram, V. Rangachari |
11.4 Quips & Sobriquets
| Laywer's paradise | Sir Ivor Jennings |
| A federation with strong centralising tendencies | Sir Ivor Jennings |
| DPSPs as "Ghosts of the Fabians" | Sir Ivor Jennings |
| cooperative federalism | Granville Austin |
| Strong centre | S. C. Kashyap |
| a case sui generis, a class and type of its own rather than an assemblage of many | C. H. Alexandrowicz |
| bargaining federalism | Morris Jones |
| quasi-federalism | K. C. Wheare |
| unitary state with federal features and not a federal state having unitary features. | K. C. Wheare |
| DPSPs as a "cheque payable by bank as per convenience" | K. T. Shah |
11.5 Parliamentary & Presidential System
| Parliamentary System | Presidential System |
|---|---|
| real executive is the cabinet or ministery | president is the chief executive |
| ministry responsible to legislature and ultimately to the voters | president is not responsible to the legislature though they have the power to impeach him |
| president occupies a position of irresponsibility | president is responsible for all executive decisions |
| doctrine of fusion of executive and legislative powers | doctrine of complete separation of powers |
| (at the same time, in Keshvananda Bharti case the Supreme Court has noted 'separation of powers' as a basic features) | doctrine of competence: each wing of the state lives and acts within its respective area without interference with the other |
12 Global programmes
| Name | Agency | Aim | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|
| REPLACE | WHO | global elimination of trans fat | |
| Earth Hour | WHO | encourage energy conservation | March 24 |
12.1 Earth Hour
- spread the message of energy conservation and generate awareness by turning off lights for one hour 08:30 to 09:30 on a particular day near the end of March
- 2018: March 24
13 Important Events in 2018
| Name of the Event | Location | Next Occurence | Agenda / Outcome | Indian Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Action Task Force | Paris | action-taken reports to be submitted to avoid sanctions | ||
14 Ramsar Convention on Wetlands 1971
It is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands. Ramsar is a city in Iran where this convention was signed in 1971. However, its headquarters are situated within the IUCN headquarters in Gland, Switzerland.
The full name of this treaty is The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance especially as Waterfowl Habitat.
The policy-makign organ for this treaty is the Conference of Contracting parties which is held every three years. The last conference was held in 2015 in Uruguay. This year the convention will be held in Dubai (UAE).
Under this treaty, a list of wetlands of international importance is maintained. At present there are 2306 such sites included.
14.1 Wetlands
Under the Ramsar Convention:
- wetlands are areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six metres
- Wetlands may incorporate riparian and coastal zones adjacent to the wetlands, and islands or bodies of marine water deeper than six metres at low tide lying within the wetlands
The World Wetland Day is celebrated on 2 February each year. The theme for 2018 was Wetlands for a Sustainable Urban Future.
14.2 Montreaux Record
It is a register of wetlands maintained as part of the Ramsar List that includes those wetland sites of international importance where changes of ecological importance have taken place, are taking place or are likely to take place in the future due to technological developments, pollution, other human activities.
There are 48 such sites at present of which 2 are in India:
| SN | Site | Waterbody | Park/Sanctuary/Reserve | State | Remark/Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keoladeo National Park (formerly Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary) | freshwater swamp | - | Rajasthan | Also a Natural World Heritage Site; Man-made wetland |
| 2 | Loktak Lake | freshwater | Keibul Lamjao National Park | Manipur | sangai deer (EN) (Manipur state animal) |
| Hoolock gibbons are found | |||||
| floating phumdis, decomposing plant material | |||||
14.3 Ramsar Sites in India
There are a total of 26 Ramsar sites in India of which 2 fall under Montreaux Record.
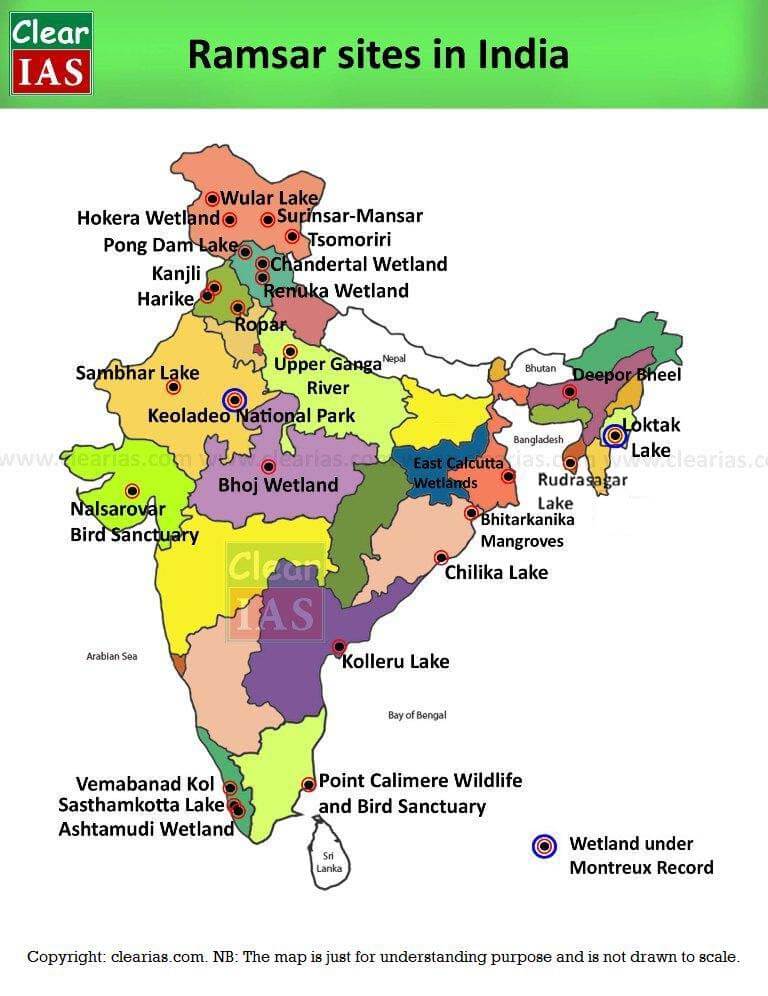
| SN | Site | Waterbody | Park/Sanctuary/Reserve | State | Remark/Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tso Moriri | ||||
| 2 | Surinsar-Mansar | J & K | |||
| 3 | Hokera | ||||
| 4 | Wular lake | ||||
| 5 | Pong Dam | ||||
| 6 | Renuka Lake | ||||
| 7 | Chandra Taal | ||||
| 8 | Harike | confluence of Satluj, Beas | Harike Wildife Sanctuary | Punjab | Man-made |
| important for migratory birds, breeding site | |||||
| 9 | Kanjli | Kali Bein | - | Punjab | man-made |
| 10 | Ropar | Satluj | - | Punjab | man-made |
| smooth indian otter, sambar, hog deer, pangolin | |||||
| 11 | Upper Ganga | Ganga (Brijghat to Narora) | Uttar Pradesh | gharial | |
| 12 | Sambhar Lake | largest inland salt lake | - | Rajasthan | pink flamingos |
| nilgai | |||||
| 13 | Keoladeo National Park | freshwater | - | Rajasthan | Man-made wetland |
| (formerly Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary) | swamp | Also a Natural World Heritage Site | |||
| 14 | Deepor Beel | freshwater lake | - | Assam | natural stormwater basin for Guwahati |
| 15 | Loktak Lake | freshwater | Keibul Lamjao National Park | Manipur | sangai deer (EN) (Manipur state animal) |
| Hoolock gibbons are found | |||||
| floating phumdis, decomposing plant material | |||||
| 16 | Rudrasagar | freshwater lake | - | Tripura | |
| 17 | Bhoj Wetland | 2 lakes – Bhojtal | - | ||
| & Lower Lake | |||||
| 18 | Nalsarovar | natural freshwater lake | Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary | Gujarat | indian wild ass |
| (relict sea) | |||||
| 19 | East Kolkata Wetland | West Bengal | |||
| 20 | Bhitarkanika | Bhitarkanika National Park | Odisha | mangroves | |
| Olive Ridley Turtles | |||||
| 21 | Chilka Lake | brackishwater lagoon | Odisha | ||
| 22 | Kolleru lake | bird sanctuary | Andhra Pradesh | ||
| 23 | Point Calimere | Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu | last remnants of dry evergreen forest | |
| 24 | Vembanad Kol | Kerala | paddy fields below sea level | ||
| 25 | Sashthamkota Lake | freshwater lake | Kerala | ||
| 26 | Ashtamudi | Kerala |
15 Punjab – Geography & Environment
15.1 Wetlands in Punjab
15.1.1 Wetlands of International Importance
| SN | Name | Waterbody | Location | Species | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harike | confluence of Beas and Satluj | Tarn Taran | man-made (Harike barrage); also a wildlife sanctuary | |
| 2 | Kanjli | river Bein (tributary of Beas) | Kapurthala | man-made (headworks across Bein); first to be declared of international importance | |
| 3 | Ropar | Satluj river | Rupnagar | man-made (barrage on Satluj) | |
15.1.2 Wetlands of National Importance
| SN | Name | Waterbody | Location | Species | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ranjit Sagar | Ranjit Sagar lake on Ravi | Pathankot | Madhopur headworks on Ravi | |
| 2 | Nangal | Nangal Lake on Satluj | Anandpur Sahib | also a wildlife sanctuary | |
15.1.3 State Wetlands
| SN | Name | Waterbody | Location | Species | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jastarwal | Harsha Chhina block, Ajnala (Amritsar) | |||
| 2 | Kahnuwan-Chamb | Gurdaspur | |||
| 3 | Keshopur-Miani | Gurdaspur | |||
| 4 | Mand-Bharthala | Nawashahr | |||
| 5 | Dholbaha Reservoir | Hoshiarpur | |||
15.1.4 Other Wetlands
Besides these there are 11 other identified wetlands in the state.
15.2 Biodiversity Conservation in Punjab
15.2.1 Conservation Reserve
| SN | Reserve | District |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rakh Sarai Amanat Khan Conservation Reserve | Tarn Taran district |
15.2.2 Two Community Reserves
| SN | Reserve | District |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keshopur-Chamb Community Reserve | Gurdaspur district |
| 2 | Lalwan Community Reserve | Hoshiarpur district |
15.2.3 Wildlife Santuaries
| SN | Name | Location | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harike | Tarn Taran | |
| 2 | Takhni-Rehmapur | Hoshiarpur | |
| 3 | Abohar | Fazlika | Black Buck |
| 4 | Bir Motibagh | Patiala | |
| 5 | Bir Gurdialpura | " | |
| 6 | Bir Bhunerheri | " | |
| 7 | Bir Mehas | Nabha (distt Patiala) | |
| 8 | Bir Dosanjh | " | |
| 9 | Bir Bhadson | " | |
| 10 | Bir Aishwan | Sangrur | |
| 11 | Jhajjar-Bachauli | Rupnagar | |
| 12 | Kathlaur Kushlian | Pathankot | |
| 13 | Nangal | Ropar | |
15.2.4 Zoological Parks
| SN | Name | Location | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mahendra Chaudhary Zoological Park (Chhat Bir Zoo) | Zirakpur | Lions |
| 2 | Ludhiana | Ludhiana | Tiger |
| 3 | Mini Zoo (Deer Park, Neelon) | Ludhiana | |
| 4 | Mini Zoo, Bir Moti Bagh | Patiala | |
| 5 | Mini Zoo, Bir Talab | Bathinda |
Animal Adoption Scheme in all 5 zoos.
15.3 Soils of Punjab
15.3.1 Bet or Khadar Soils (Flood Plains)
These are found along the rivers, streams and choes and are very fertile. They have low organic content and are deep, stratified and wet. They support wheat, paddy, vegetables, sugarcane.
They are found along Satluj, Ravi, Beas, Ghaghar, Bein, etc.
15.3.2 Loamy Soils
These are the most fertile soils in the state, suitable for cultivation of paddy and wheat. They are deep grained, fine and develop under sub-moist and warm temperature.
They are predominantly found in Nawashahr, Nakodar, Kapurthala, Phagwara. In Amritsar and Batala, their fertility has been affected by over-irrigation, choes and rivulets.
15.3.3 Sierozams
They comprise 25% of the soils in the state. These are grey and deficient in organic matter. They are fine grained and loamy. With proper irrigation they produce the highest yield of wheat.
Found in long belts from Mukerian-Tanda, Nakodar-Phillaur, Tarn Taran-Patti, Fatehgarh Sahib, Rajpura.
15.3.4 Kandi soils
They are coarser and rougher soils that are found alongside the Shivaliks. They are dominated by gravel and pebbles.
Found in Gurdaspur, Pathankot, Hoshiarpur, Nawashahr, Ropar.
15.3.5 Sandy soils
Result of semi-arid conditions
poor in NPK, capable of producing cotton, citrus fruits, oilseeds, wheat and other fodder crops.
15.3.6 Desert soils
Result of desert conditions. Poor in NPK, calcerous in nature due to high evaporation. Covered by wind-blown sands.
suitable for cotton, moth, citrus, wheat, bajra, kharif fodder
15.3.7 Podzolic / Forest soils
erosion by running water in rugged topography. Gurdaspur, Hoshiarpur, Pathankot, Nawashahr, Ropar.
15.3.8 Sodic and Saline
along Bikaner land in Abohar, Bathinda. High sodium content and stron alkaline nature.
15.4 Rivers of Punjab
15.4.1 Perennial
| Name | Ancient Name | Greek Name | Dams | Head | Mouth | Tributaries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jhelum | Vitasta | Hydapses | Mangla Dam, Uri Dam, Kishanganga Dam | Verinag Spring | Chenab | Lidder, Neelam, Sindh |
| Chenab | Chandrabagh, Iskamati | Acesinas | Baglihar | Bara Lachha pass | Panjnad | Marusadar |
| Ravi | Purushini, Irawati | Hydraotes | Ranjit Sagar, Chamera, Shahpur Kandi (under construction) | Chamba District | Chenab | Ujh, Siul |
| Beas | Vipas, Arjiki | Hyphasis | Pong, Pandoh | Beas Kund, Rohtang Pass (Kullu District) | Satluj at Harike | Bein |
| Satluj | Shatadru, Satlutri | Heisdros | Bhakra-Nangal, Karcham Wangtoo, Nathpa Jhakhri | Langqên Zangbo (near Lake Rakshastal), Tibet | Panjnad | Spiti, Beas; Baspa |
| Indus | Sindhu | Indos | Mansarovar Lake | Arabian Sea (primary), Rann of Kachh (secondary) | Ravi, Beas, Satluj, Jhelum, Chenab, Ghaghar Hakra, Zaskar, Suru, Soan, Luni; Shyok, Hunza, Gilgit, Swat, Kunar, Kabul, Kurram, Gomal, Zhob | |
| Kali Bein | spring in Dhanoa (Hoshiarpur) | Beas | Chhoti Bein |
15.4.2 Ephemeral
| Name | Ancient Name | Greek Name | Dams | Head | Mouth | Tributaries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ghaggar-Hakra | Ottu Barrage (Harayana), Kaushalya Dam | shivalik hills | ottu barrage | Kasuhalya | ||
| (called Ghaggar in India, Hakra in Pakistan (now dried) |